Data Insights: The Basics of Data Warehousing
Introduction
Modern businesses generate massive amounts of data from apps, transactions, and customer interactions. But raw data by itself isn’t useful until it’s structured, cleaned, and made available for insights. That’s where a data warehouse comes in — a system designed to consolidate data from multiple sources for analysis and decision-making.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a centralized repository that stores structured data from different systems. Unlike operational databases (used for day-to-day transactions), data warehouses are optimized for queries, reporting, and analytics.
- Operational DBs (OLTP): Fast inserts/updates (e.g., e-commerce orders).
- Data Warehouses (OLAP): Fast queries/aggregations (e.g., monthly sales trends).
Core Components of a Data Warehouse
- Data Sources
- Applications, IoT devices, CRM, ERP, logs.
- ETL/ELT Process
- Extract data, Transform/clean it, Load into warehouse.
- Tools: AWS Glue, Apache Airflow, dbt.
- Data Storage
- Central warehouse like Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, or Google BigQuery.
- Analytics & BI Tools
- Tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker that connect to the warehouse.
Why Use a Data Warehouse?
- Single Source of Truth: Consolidates scattered data.
- Historical Analysis: Store years of data for long-term trends.
- Faster Decision-Making: Prepares data for dashboards and reports.
- Scalability: Handle terabytes or petabytes of data efficiently.
Diagram: The Basics of Data Warehousing
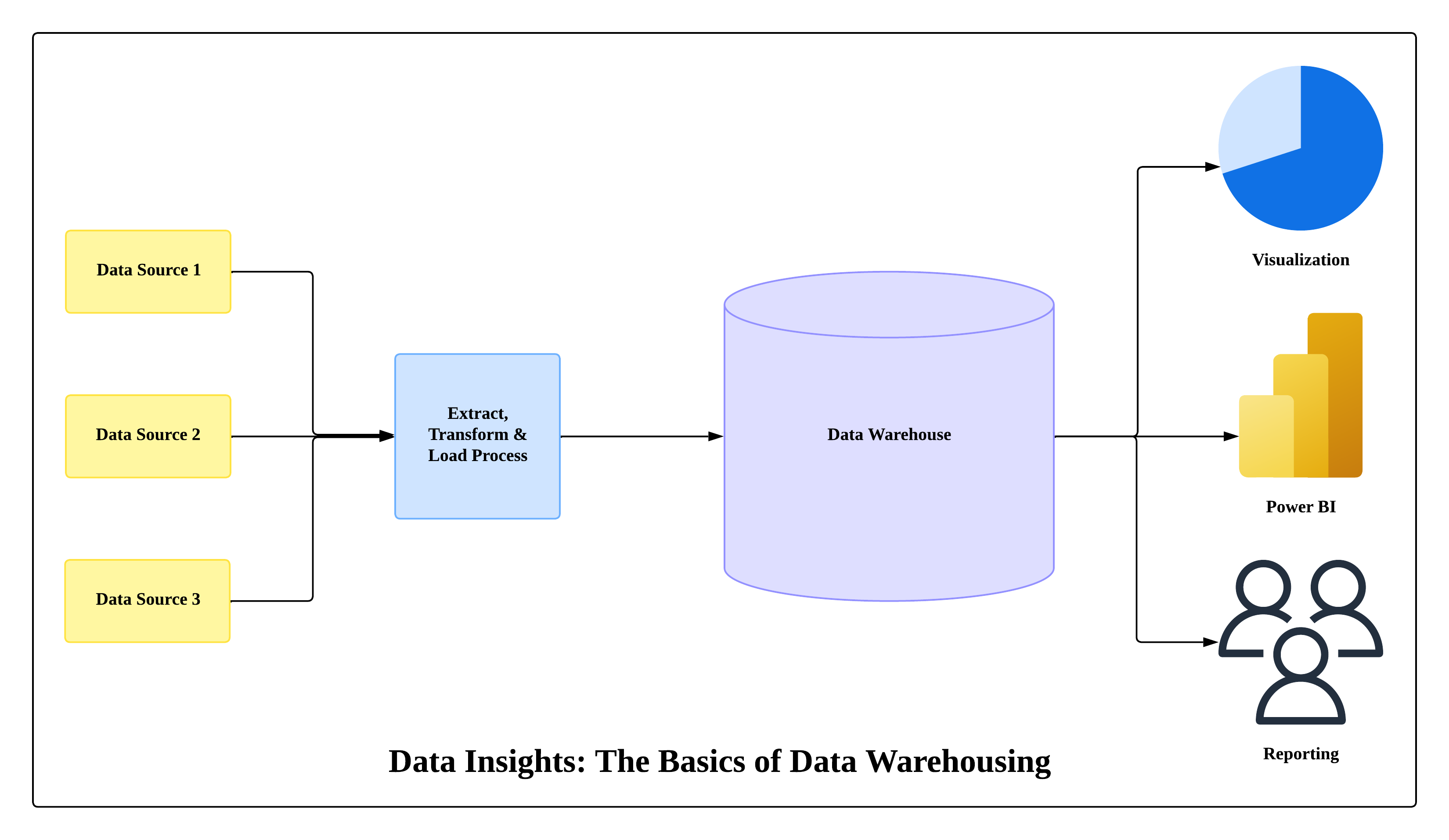
Figure: The Basics of Data Warehousing
Common Data Warehousing Architectures
- Star Schema: Central fact table linked to dimension tables (simplifies queries).
- Snowflake Schema: More normalized version, reduces redundancy.
- Data Lakehouse: Hybrid of data lakes + data warehouses for structured and semi-structured data.
Pro Tip
Start small with a managed cloud data warehouse (like Redshift Serverless or BigQuery) instead of building heavy on-prem systems. You’ll save on infrastructure costs and scale more easily.
Takeaway
A data warehouse is the backbone of modern analytics, providing a centralized, structured, and optimized platform for decision-making. By combining ETL processes, scalable storage, and BI tools, it helps organizations unlock the real value of their data.




No comments yet. Be the first to comment!